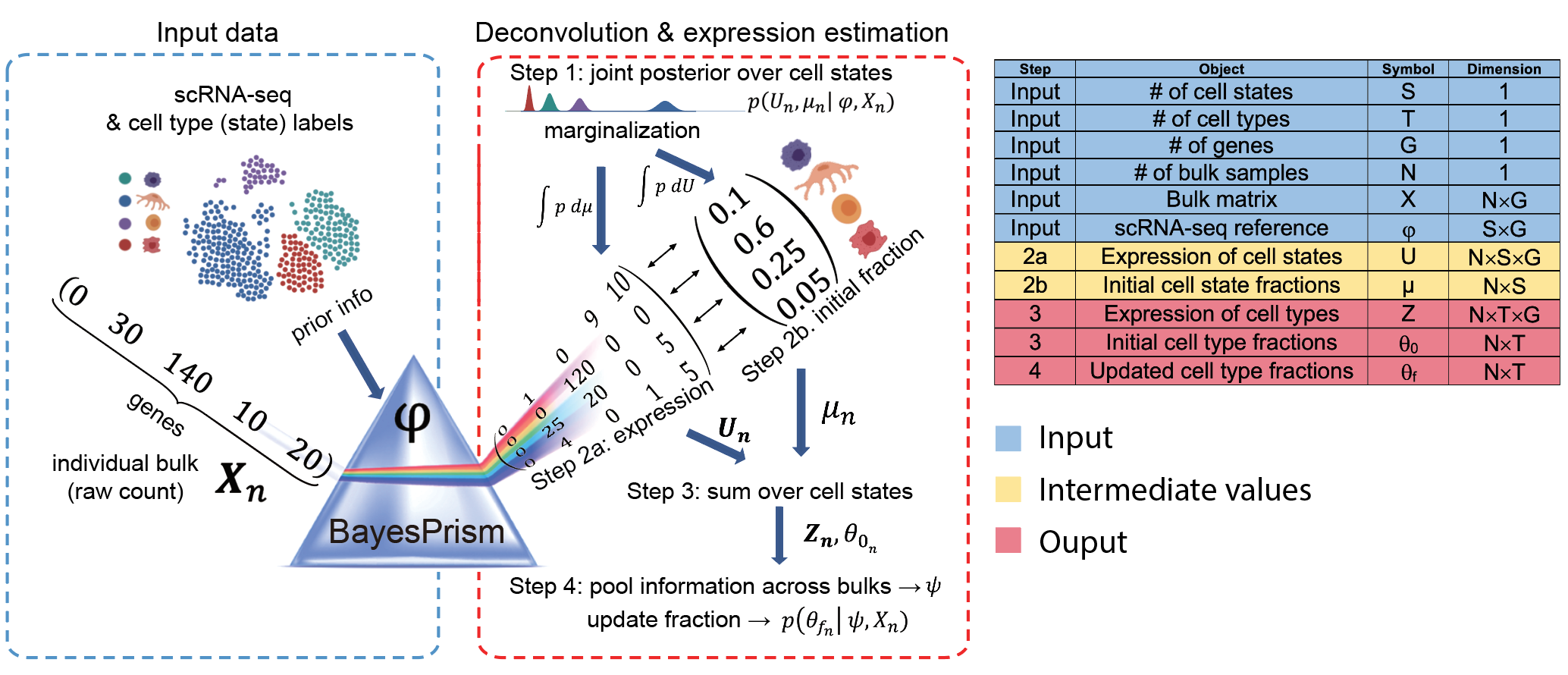
BayesPrism是由美国康奈尔大学Tin Yi Chu等人开发的R包工具,于2022年4月发表在Nature Cancer。简单来说,该方法使用单细胞RNA-seq作为先验信息,通过估计批量样本中细胞类型比例和细胞类型特异性基因表达的联合后验分布。P(θ,Z|X,ϕ),参数概念如下
- ϕ:输入数据 – 单细胞表达矩阵,及相关注释结果;
- X:输入数据 – Bulk RNA-seq表达矩阵;
- θ:输出结果 – Bulk样本的细胞组成;
- Z:输出结果 – 每一种细胞类型的Bulk基因表达矩阵。
DOI:https://www.nature.com/articles/s43018-022-00356-3
Github:https://github.com/Danko-Lab/BayesPrism
1、安装R包#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
|
# 检查是否安装相关依赖包
for (pkg in c("snowfall", "NMF", "gplots", "scran", "BiocParallel")){
print(requireNamespace(pkg, quietly = TRUE))
}
# install.packages("snowfall")
# install.packages("NMF")
# install.packages("gplots")
# BiocManager::install("scran")
# BiocManager::install("BiocParallel")
# 在线或下载到本地安装
# https://github.com/Danko-Lab/BayesPrism/tree/main
# list.files("BayesPrism-main/BayesPrism/")
# # [1] "DESCRIPTION" "inst" "man" "NAMESPACE" "R"
devtools::install_local("BayesPrism-main/BayesPrism/")
|
2、示例数据#
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
33
34
35
36
|
load("./BayesPrism-main/tutorial.dat/tutorial.gbm.rdata")
## (1) Bulk RNA-seq
dim(bk.dat)
# [1] 169 60483
bk.dat[1:4,1:2]
# ENSG00000000003.13 ENSG00000000005.5
# TCGA-06-2563-01A-01R-1849-01 5033 12
# TCGA-06-0749-01A-01R-1849-01 3422 62
# TCGA-06-5418-01A-01R-1849-01 4976 17
# TCGA-06-0211-01B-01R-1849-01 5770 5
## (2) scRNA-seq
dim(sc.dat)
# [1] 23793 60294
sc.dat[1:4,1:2]
# ENSG00000130876.10 ENSG00000134438.9
# PJ016.V3 0 0
# PJ016.V4 0 0
# PJ016.V5 0 0
# PJ016.V6 0 0
## (3) 主要细胞类型注释结果
str(cell.type.labels)
# chr [1:23793] "tumor" "tumor" "tumor" "tumor" "tumor" "tumor" "tumor" ...
sort(table(cell.type.labels))
# tcell oligo pericyte endothelial myeloid tumor
# 67 160 489 492 2505 20080
## (4) 细胞亚群注释结果
str(cell.state.labels)
# chr [1:23793] "PJ016-tumor-0" "PJ016-tumor-0" "PJ016-tumor-3" ...
sort(table(cell.state.labels)) %>% head
# PJ017-tumor-6 PJ032-tumor-5 myeloid_8 PJ032-tumor-4 PJ032-tumor-3
# 22 41 49 57 62
|
*表达数据均推荐使用raw count;另外相当于细胞亚型的state标签,要确保每一类亚型要有一定量的细胞(>20)
3、单细胞数据质控#
3.1 细胞注释的合理性
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
plot.cor.phi(input=sc.dat,
input.labels=cell.state.labels,
title="cell state correlation",
#specify pdf.prefix if need to output to pdf
#pdf.prefix="gbm.cor.cs",
cexRow=0.2, cexCol=0.2,
margins=c(2,2))
plot.cor.phi(input=sc.dat,
input.labels=cell.type.labels,
title="cell type correlation",
#specify pdf.prefix if need to output to pdf
#pdf.prefix="gbm.cor.ct",
cexRow=0.5, cexCol=0.5)
|
3.2 筛选基因
- 删除核糖体,线粒体,性染色体等基因,以及低表达基因
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
sc.dat.filtered <- cleanup.genes(input=sc.dat,
input.type="count.matrix",
species="hs",
gene.group=c( "Rb","Mrp","other_Rb","chrM","MALAT1","chrX","chrY") ,
exp.cells=5)
dim(sc.dat.filtered)
# [1] 23793 31737
|
1
2
3
4
|
sc.dat.filtered.pc <- select.gene.type(sc.dat.filtered,
gene.type = "protein_coding")
dim(sc.dat.filtered.pc)
# [1] 23793 16148
|
4、BayesPrism预测#
4.1 构建prism对象
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
|
myPrism <- new.prism(
reference=sc.dat.filtered.pc,
mixture=bk.dat,
input.type="count.matrix",
cell.type.labels = cell.type.labels,
cell.state.labels = cell.state.labels,
key="tumor", #如若有肿瘤细胞类型,需要在此交代
outlier.cut=0.01,
outlier.fraction=0.1,
)
|
4.2 prism预测
1
2
3
|
# 耗时
bp.res <- run.prism(prism = myPrism, n.cores=50)
# save(bp.res, file="bp.res.rda")
|
4.3 提取结果
1
2
3
4
5
6
|
theta_type = get.fraction(bp.res,
which.theta="final", #c("first", "final")
state.or.type="type" #c("state", "type")
)
dim(theta_type)
# [1] 169 6
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
Z_tumor = get.exp(bp.res,
state.or.type="type", # c("state", "type")
cell.name = "tumor")
dim(Z_tumor)
# [1] 169 16145
dim(bk.dat)
# [1] 169 60483
|
5、肿瘤模块NMF分析#
- 因十分耗时,暂时仅记录如下。如需用到可参考Github介绍
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
Z.tum.norm <- t(bp.res@reference.update@psi_mal)
dim(Z.tum.norm)
# [1] 16145 169
estim.Z.tum.norm <- nmf(Z.tum.norm, rank=2:12, seed=123456)
plot(estim.Z.tum.norm)
consensusmap(estim.Z.tum.norm, labCol=NA, labRow=NA)
ebd.res <- learn.embedding.nmf(bp = bp.res,
K = 5,
cycle = 50,
compute.elbo = T)
|
6、注意事项#
根据Github的FAQ部分总结相关注意点如下:
**(1)**应该使用包含肿瘤组织全部细胞类型的完整scRNA-seq数据作为参考。对于第一级的细胞标签(type),如果明确细胞亚型已知(例如CD4+ T等),应当用之。更高分辨率的注释可以做为第二级的state;
**(2)**对于tumor细胞的第二级注释,推荐在每个样本内进行再聚类分析。
**(3)**在包含肿瘤细胞的参考数据中,需要注意肿瘤细胞与高度类似于肿瘤细胞的正常细胞关系。例如分析胶质母细胞瘤(GBM)时,将正常星形细胞纳入参考可能导致对星形细胞的过高估计和恶性细胞的低估。但不影响其它细胞类型的分析。
