题目:In Silico Prediction and Insights Into the Structural Basis of Drug Induced Nephrotoxicity
期刊 | 日期:05 January 2022
DOI: 10.3389/fphar.2021.793332
简括:建立机器学习模型的经典流程,值得注意的是包括化合物特征提取,模型建立/评价都是在online chemical database and modeling environment (OCHEM)平台完成的。文章建立的模型也上传到该平台中:https://ochem.eu/article/140251
1、收集数据
1.1 标签数据
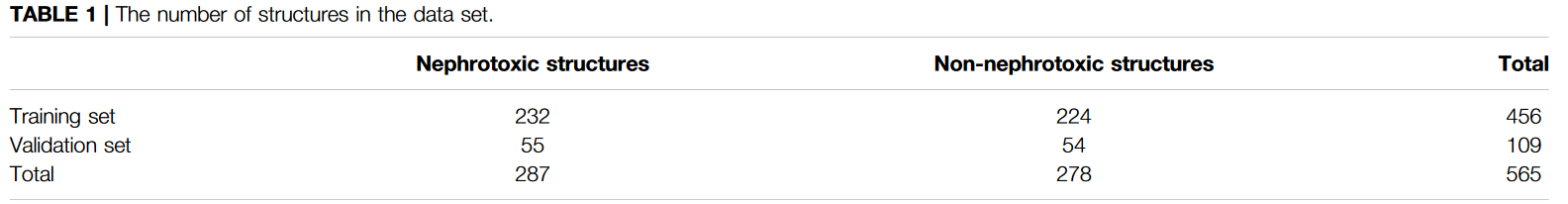
如下,最终收集到565个药物(287, 278)
(1)阳性数据,即肾毒性药物,收集自SIDER数据库:drugs with nephrotoxicity related ADRs with frequency ≥0.1%;
(2)阴性数据,即无肾毒性药物参考2019年Zhang等预测模型所使用的阴性药物;
(3)筛选不合适的药物:去重、混合物主要成分、salt → parent form
1.2 特征数据
基于OCHEM平台,计算8种分子描述符(molecular descriptors)
- Chemaxon descriptors (Chemaxon, 499 descriptors)
- Fragmentor
- GSFrag descriptors (GSFrag, 1,138 descriptors)
- MORDRED descriptors (MORDRED, 1826 descriptors),
- PyDescriptor (1,624 descriptors),
- QNPR descriptors (QNPR)
- RDKit descriptors (RDKit)
- alvaDesc descriptors (5,666 descriptors)
对于深度学习模型,直接使用SMILES字符串作为每个化合物输入
2、训练模型
2.1 模型算法
(1)5种机器学习模型
- associative neural network (ASNN)
- support vector machine (SVM)
- C4.5 decision tree
- random forest (RFR)
- extreme gradient boosting (XGBoost)
(2)5种深度学习模型
- convolutional neural network fingerprint (CNF)
- transformer convolutional neural network (TRANSNN)
- TEXTCNN algorithm available from DeepChem (TEXTCNN)
- Graph Isomorphism Network (GIN)
- edge attention based multirelational graph convolutional networks (EAGCNG)
2.3 评价指标
AUC
total accuracy(Q)
sensitivity(SE)
specificity(SP)
enrichment factor(EF)
Matthews correlation coefficient(MCC)
2.2 数据集划分
(1)如下划分出训练集与验证集:
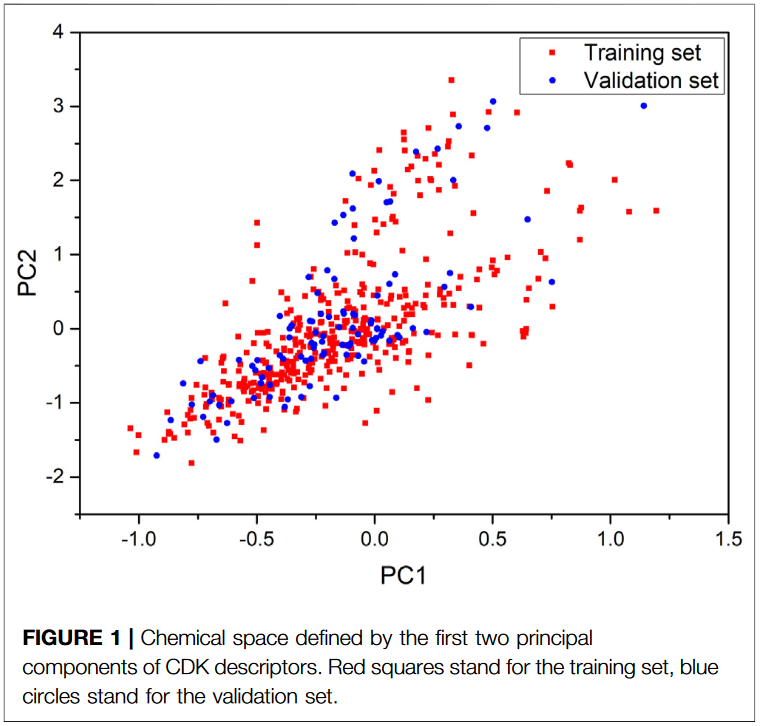
(2)经降维分析,发现两组数据分布均匀。
2.3 训练模型
- 使用训练集,经5折交叉验证训练出40个机器学习模型(5×8)与5个深度学习模型
- 基于Q>0.7, AUC>0.8发现3个最优模型:2个ML(XGBoost_QNPR, RFR_QNPR)与1个DL(CNF)
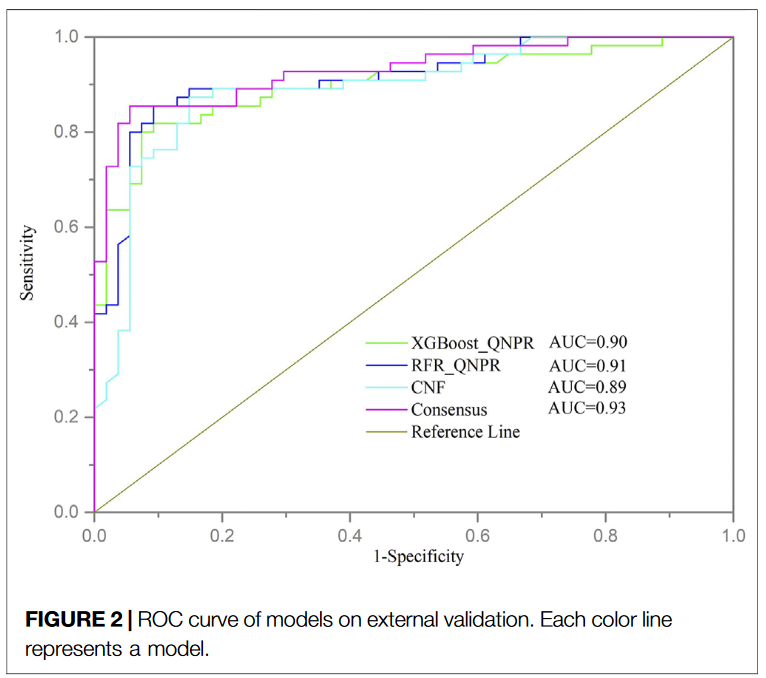
- 使用上述3个Top模型进行consensus modeling,即3个模型预测结果的均值,性能有较大提示。
2.4 验证模型
- 对上述3个Top模型以及consensus模型进行测试集验证,发现还是consensus模型较优。